In this post, you will see how to write a program for the Addition of Two Matrix in Java. Here, we will show you two examples, one with two static matrices, and another one with dynamic matrices.
Rules for the Addition of two Matrix:
- The addition of matrix can be done when the dimensions of the matrices are the same.
- Matrix addition is the operation of adding two matrices by adding the corresponding entries together.
- The resultant matrix dimension will be the same as matrix1 and matrix2.
Addition of two matrix Example:
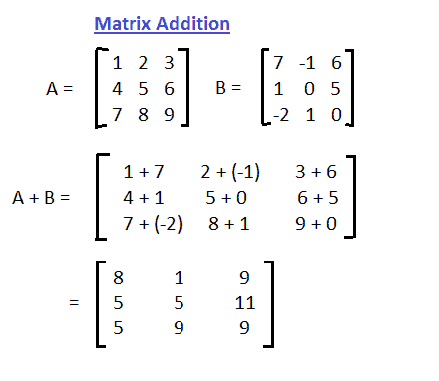
Example-1: Addition of Matrices in Java
package com.javacodepoint.array.multidimensional;
/**
* Matrix Addition Example
*/
public class AddTwoMatrix {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare and Initialize
// two Matrices of dimension 3x2
int matrix1[][] = { { 1, 2 },
{ 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6 }
};
int matrix2[][] = { { 1, 2 },
{ 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6 }
};
// Declare third matrix of same dimension 3x2
// to store the addition of two matrices
int matrix3[][] = new int[3][2];
// Add two matrices
for (int i = 0; i < matrix1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix1[0].length; j++) {
matrix3[i][j] = matrix1[i][j] + matrix2[i][j];
}
}
// Print the result matrix
System.out.println("The resultant Matrix3 =>");
for (int i = 0; i < matrix3.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix3[0].length; j++) {
System.out.print(matrix3[i][j] + " ");
}
// move cursor to new row/line
System.out.println();
}
}
}
OUTPUT:
The resultant Matrix3 =>
2 4
6 8
10 12
Example-2: Addition of two Matrix using Scanner in Java
package com.javacodepoint.array.multidimensional;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* Matrix Addition Example using Scanner
*/
public class AddTwoMatrix2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare variables for matrix dimension
int row1, col1, row2, col2;
// Creating scanner object for reading user input
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the first matrix dimension,");
System.out.print("Row= ");
row1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("Column= ");
col1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the second matrix dimension,");
System.out.print("Row= ");
row2 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("Column= ");
col2 = sc.nextInt();
if (row1 != row2 || col1 != col2) {
System.out.println("Addition of Matrices is not possible. Dimensions of both matrices should be same!");
return;
}
// Declare three Matrices
int matrix1[][] = new int[row1][col1];
int matrix2[][] = new int[row2][col2];
int matrix3[][] = new int[row1][col1]; // can be take row2/col2 as well
// Read the user inputs for matrix1
System.out.println("Enter Matrix1 (" + row1 + "x" + col1 + "),");
for (int i = 0; i < row1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col1; j++) {
System.out.print("Enter value for [" + i + "][" + j + "]= ");
matrix1[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
// Read the user inputs for matrix2
System.out.println("Enter Matrix2 (" + row1 + "x" + col1 + "),");
for (int i = 0; i < row2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col2; j++) {
System.out.print("Enter value for [" + i + "][" + j + "]= ");
matrix2[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
// Add two matrices
for (int i = 0; i < row1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col1; j++) {
matrix3[i][j] = matrix1[i][j] + matrix2[i][j];
}
}
// Print the result matrix
System.out.println("The resultant Matrix3 (" + row1 + "x" + col1 + "),");
for (int i = 0; i < row1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col1; j++) {
System.out.print(matrix3[i][j] + " ");
}
// move cursor to new row/line
System.out.println();
}
}
}
OUTPUT:
Enter the first matrix dimension,
Row= 2
Column= 3
Enter the second matrix dimension,
Row= 2
Column= 3
Enter Matrix1 (2×3),
Enter value for [0][0]= 1
Enter value for [0][1]= 2
Enter value for [0][2]= 3
Enter value for [1][0]= 4
Enter value for [1][1]= 5
Enter value for [1][2]= 6
Enter Matrix2 (2×3),
Enter value for [0][0]= 1
Enter value for [0][1]= 2
Enter value for [0][2]= 3
Enter value for [1][0]= 4
Enter value for [1][1]= 5
Enter value for [1][2]= 6
The resultant Matrix3 (2×3),
2 4 6
8 10 12
See also:
Java Program to Subtract the Two Matrices.
Java Program to Find the Sum of an Array.
Java Program to Count the Number of Vowels in a String.
