Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a fundamental technology that plays a crucial role in web development. It is used to define the visual presentation and layout of HTML documents, enhancing the overall user experience. CSS can be implemented in various ways, depending on the scope and requirements of the project. In this article, we will explore the three main types of CSS: Inline, Internal, and External, and understand when and how to use each effectively.
Table of Contents
What are the different types of CSS?
There are three types of CSS:
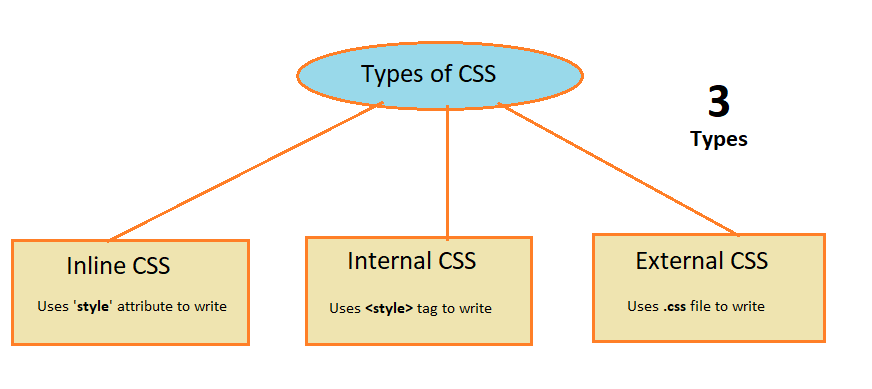
3 Types of CSS with Examples
Inline CSS
Inline CSS is generally used to style a specific HTML element only. We can write inline CSS simply by adding the style attribute to each HTML element.
For Example:
<h1 style="background-color:yellow;"> This is a heading </h1>
<p style="color:red"> This is some pragraph </p>
This CSS type is not recommended, as each HTML tag needs to be styled individually. Managing a website may be difficult if we use only inline CSS.
Advantages
- You can easily and quickly write inline CSS to an HTML page.
- It is useful for testing or previewing the changes, and performing quick fixes to your website.
- You don’t need to create or link a separate document as required in the external CSS.
Disadvantages
- Generally, Inline CSS needs to be written in each HTML tag individually. So managing a website may be difficult if we use only inline CSS.
- Adding CSS property to every HTML tag is time-consuming.
- Styling multiple elements can affect your page’s size and download time.
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1 style="color:red">Simple Box Design </h1>
<div style="height:200px;width:300px;background-color:yellow"> </div>
</body>
</html>
Internal CSS
Internal CSS is also known as embedded CSS. It is generally used to style a single page. We can write internal CSS inside a <style> tag within the HTML pages.
For Example:
<style>
h1{
background-color : yellow;
color : red;
}
</style>
<h1> This is a heading </h1>
This CSS type is an effective method of styling a single page. However, using this style for multiple pages is time-consuming as you need to put CSS style on every page of your website.
Advantages
- You can use ID and class selectors to write the internal CSS.
- Since you’ll only add the code within the same HTML file, you don’t need to create or upload multiple files.
Disadvantages
- Since you’ll only add the code within the same HTML file, styling multiple pages will become time-consuming.
- Adding the code to the HTML document can increase the page’s size and loading time.
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* Using tag name as a selector here */
h1{
background-color:orange;
}
/* Using class as a selector here */
.box{
height:200px;
width:300px;
background-color:yellow;
}
/* Using ID as a selector here */
#circle{
height:200px;
width:200px;
background-color:red;
border-radius:50%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Simple example of internal CSS</h1>
<div class="box"></div>
<div id="circle"></div>
</body>
</html>
External CSS
With an external CSS, you can change the look of an entire website by changing just one file. We can write external CSS in a separate .css file. Each HTML page must include a reference to the external CSS file inside the <link> tag, inside the <head> tag.
For Example:
creating a my-style.css file with any text editor( eg:- Notepad++)
/* Using tag name as a selector here */
h1{
background-color:orange;
}
/* Using class as a selector here */
.box{
height:200px;
width:300px;
background-color:yellow;
}
/* Using ID as a selector here */
#circle{
height:200px;
width:200px;
background-color:red;
border-radius:50%;
}
Now include the my-style.css external file in your HTML page using <link> tag:
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="my-style.css" />
The complete HTML page will look like this:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="my-style.css" />
</head>
<body>
<h1>Simple example of external CSS</h1>
<div class="box"></div>
<div id="circle"></div>
</body>
</html>
Advantages
- Since the CSS code is in a separate file, your HTML files will have a cleaner structure and be smaller in size.
- You can use the same .css file for multiple pages when you want the same look for each page.
Disadvantages
- Your pages may not be rendered correctly until the external CSS is loaded.
- Uploading multiple external CSS files can increase the download time of a website.
Difference between the 3 types of CSS styles
The below table shows you the difference between inline or embedded and external CSS. Internal CSS is also known as embedded CSS.
| Inline CSS | Internal CSS | External CSS |
|---|---|---|
| Inline CSS is used to style a specific HTML element. | Internal CSS is used to style a specific HTML page. | External CSS is used to change the look of an entire website by changing just one file. |
| You can write inline CSS using the style attribute. | You can write Internal CSS using the <style> tag. | You can write External CSS in a .css file. |
| It doesn’t allow you to use any selectors. | It allows you to use selectors. eg:- id, class, tag name, etc. | It also allows you to use selectors. |
| It takes time to use as each element needs to be added. | It is also time-consuming but in comparison to Inline CSS is less. | It saves time as you can use the same file on multiple pages for the same look. |
Which is Commonly used in CSS?
All three methods of applying CSS styles—inline, external, and internal—are commonly used, depending on the requirements of the website or web application. However, external CSS is the most popular as it separates content and presentation, facilitating easier maintenance and updates across multiple pages.
Inline CSS is typically reserved for small, specific changes to individual elements, but excessive use can clutter HTML and hinder readability.
Internal CSS is employed for styles specific to a page or section, offering tailored design without affecting the entire site.
The choice among these methods depends on project needs: Inline CSS is quick but cumbersome to manage, external CSS is widely favored for consistency and control, while internal CSS suits cases requiring unique styles for particular elements or pages.
CSS Priority
CSS priority is also known as CSS specificity. An HTML element can be targeted by multiple CSS rules. If the same CSS property is defined multiple times with different-different values then the browser will apply one value based on priority. This is what CSS priority is about.
For better understanding, let’s take an example here,
<p id="first-paragraph" class="paragraph"> This is a sample paragraph </p>
Now let’s define multiple CSS rules for it:
1.) Defining CSS rule using the ID selector
#first-paragraph{
color : red;
}
2.) Defining CSS rule using the Class selector
.paragraph{
color : blue;
}
3.) Defining CSS rule using Tag name selector
p{
color : green;
}
Because the browser can apply only one color to this paragraph, it will have to decide which CSS rule takes priority over other ones.
In the above example, the browser will apply the color red because #id selector has more priority than others.
How does CSS Priority work?
The browser prioritizes applying CSS rules based on the CSS type and selector. Let’s understand one by one in detail:
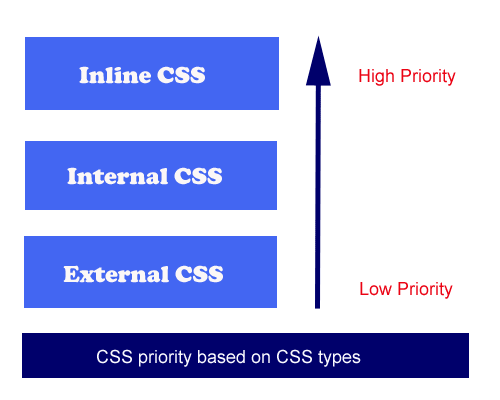
Priority based on CSS type
The browser will decide the priority based on three types of CSS (inline, internal, and external). The below image shows the priority among these three types:
Let’s take an HTML element heading <h1> for example:
<h1> This is a sample Heading </h1>
Let’s define CSS rules of all three types (Inline, Internal, and External) and see the output:
First create a .css document file (eg: my-style.css) and write the below CSS rules:
/* defining external css rules */
h1{
background-color:yellow;
}
Example (Defined all three types)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- Externally defined CSS rules adding to the HTML page -->
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="my-style.css" />
<style>
/* Defining Internal CSS */
h1{
background-color:blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Defining Inline CSS -->
<h1 style="background-color:green"> This is a sample Heading </h1>
</body>
<html>
Output
This is a sample Heading
In the above example, Inline CSS has more priority than others which is why the browser has applied the background color green.
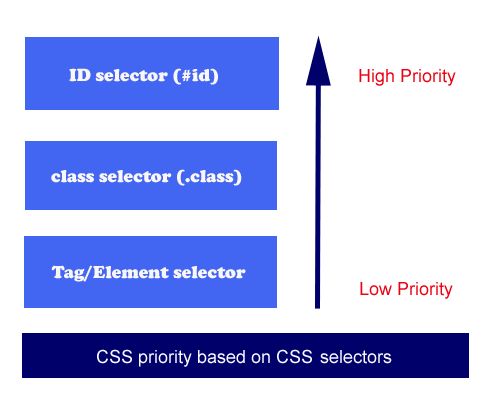
Priority based on CSS selector
The browser will also decide the priority based on CSS selectors (eg: #id, .class, and Tag name). The below image shows the priority among the selectors:
Let’s take an HTML element heading <h1> with id and class attribute for example:
<h1 id="my-heading" class="title"> This is a sample Heading </h1>
Example (Defined all selectors)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* Defining CSS rule using id selector */
#my-heading{
color : red;
}
/* Defining CSS rule using class selector */
.title{
color : blue;
}
/* Defining CSS rule using tag name selector */
h1{
color : green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 id="my-heading" class="title"> This is a sample Heading </h1>
</body>
<html>
Output
This is a sample Heading
In the above example, the #id selector has more priority than others that’s why the browser has applied the red color.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of CSS and their appropriate use is essential for efficient and maintainable web development. Inline CSS is useful for quick and temporary styling, while Internal CSS strikes a balance between specificity and modularity. However, for larger projects with multiple pages, External CSS is the most recommended approach, as it promotes code reusability and consistent styling.
Learn more about CSS Priority here: CSS Priority.
CSS Reference: Cascading Style Sheets
FAQs
What are the 3 types of CSS?
There are three types of CSS inline, internal, and external CSS.
What are the 3 ways to style in CSS?
There are 3 distinct methods for styling in CSS, Local style, Page-Level style, and External Style. Each level of styling is given a different hierarchical priority and is used for different reasons.
Related Articles:
- CSS Priority
- CSS – Color Names and Color Codes
- CSS – Most common CSS properties Part-1
- CSS – Most common CSS properties Part-2
