Spring Boot Kafka Integration: Apache Kafka is one of the most powerful distributed messaging systems used in modern microservices and event-driven architectures. In this tutorial, we will learn how to integrate Kafka with Spring Boot using minimal configuration.

Table of Contents
Setting Up Kafka Locally or Using Docker
Before writing any code, you need a Kafka broker running locally. You can either:
1. Install Kafka manually
Download Kafka from the Apache Kafka official site, extract it, and start Zookeeper and the Kafka server. You can see our details Guide here: Setting Up Apache Kafka Locally
2. Run Kafka with Docker
# docker-compose.yml
version: '3'
services:
zookeeper:
image: wurstmeister/zookeeper
ports:
- "2181:2181"
kafka:
image: wurstmeister/kafka
ports:
- "9092:9092"
environment:
KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS: PLAINTEXT://localhost:9092
KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT: zookeeper:2181
Run using Docker command:
docker-compose up -d
At this point, Kafka should be up and running.
Creating a Spring Boot Kafka Application using Spring Initializr
The easiest way to start is with Spring Initializr.
Steps to create a Spring Boot Kafka Application:
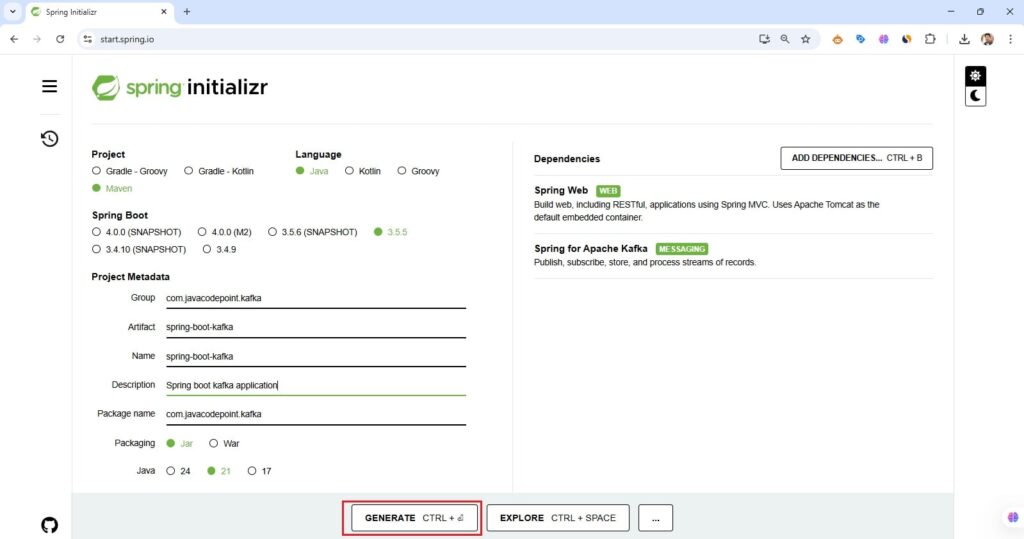
- Open Spring Initializr.
- Select the following options:
- Project: Maven
- Language: Java
- Spring Boot:
3.5.0(or latest) - JDK: 17+
- Dependencies:
- Spring for Apache Kafka
- Spring Web (optional, for REST APIs)
- Click Generate to download the project.
- Extract the zip file.
Importing the Project into IntelliJ IDEA CE
- Open IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition. (If not installed, follow the guide here: Install IntelliJ IDEA)
- Click File → Open.. → Select extracted Spring Boot project folder.
- IntelliJ will import the Maven project and download the required dependencies.
- Verify that the project builds successfully by running the following Maven command in IntelliJ Terminal:
- mvn clean install
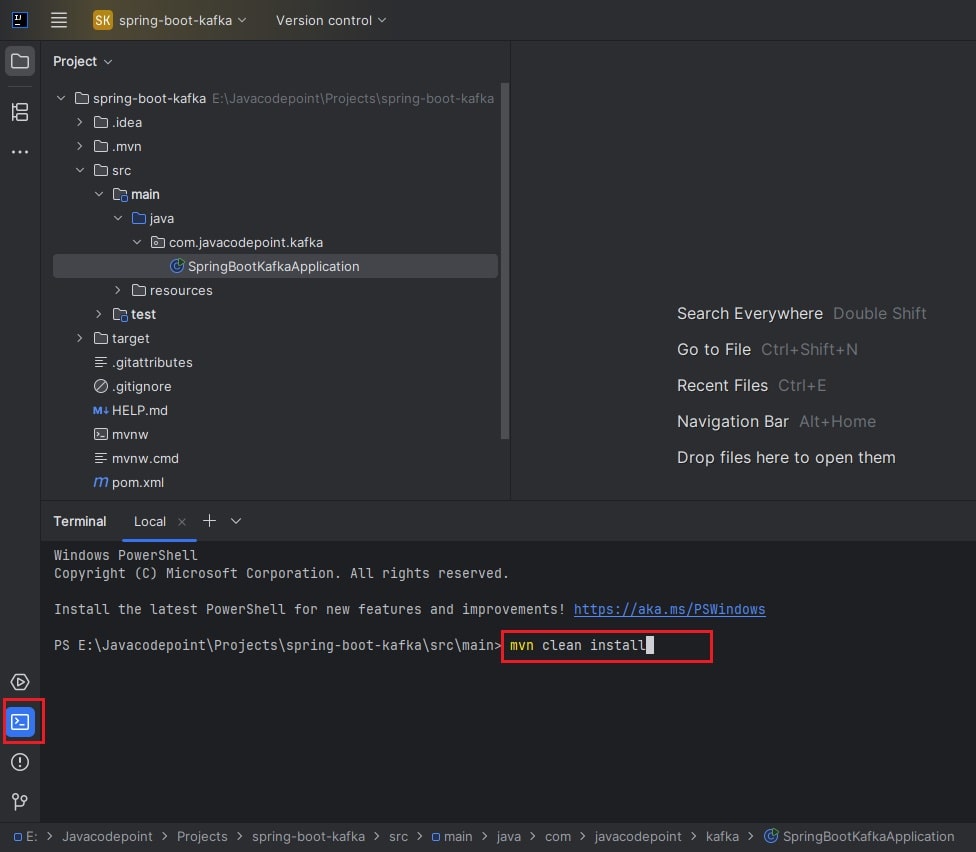
Now you have a Spring Boot Kafka project ready to code.
Adding Kafka Dependencies in pom.xml
If you forgot to add dependencies during project generation, add them manually:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>
Configuring Kafka in Spring Boot
You can configure it in either the application.properties or the application.yml file
In src/main/resources/application.properties:
spring.application.name=spring-boot-kafka
spring.kafka.bootstrap-servers=localhost:9092
# Producer configuration
spring.kafka.producer.key-serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
spring.kafka.producer.value-serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
# Consumer configuration
spring.kafka.consumer.group-id=my-group
spring.kafka.consumer.key-deserializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
spring.kafka.consumer.value-deserializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
spring.kafka.consumer.auto-offset-reset=earliestIn src/main/resources/application.yml:
spring:
kafka:
bootstrap-servers: localhost:9092
consumer:
group-id: my-group
auto-offset-reset: earliest
key-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
value-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
producer:
key-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
value-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
Creating a Kafka Producer
package com.javacodepoint.kafka;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class MessageProducer {
private final KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate;
public MessageProducer(KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate) {
this.kafkaTemplate = kafkaTemplate;
}
public void sendMessage(String topic, String message) {
kafkaTemplate.send(topic, message);
System.out.println("Sent message: " + message + " to topic: " + topic);
}
}
Creating a Kafka Consumer
package com.javacodepoint.kafka;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.KafkaListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class MessageConsumer {
@KafkaListener(topics = "test-topic", groupId = "my-group")
public void listen(String message) {
System.out.println("Received message: " + message);
}
}
Creating a Controller to Test a Kafka Application
package com.javacodepoint.kafka;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/kafka")
public class MessageController {
private final MessageProducer producer;
public MessageController(MessageProducer producer) {
this.producer = producer;
}
@GetMapping("/send")
public String sendMessage(@RequestParam String message) {
producer.sendMessage("test-topic", message);
return "Message sent: " + message;
}
}
Testing the Kafka Message Flow using Postman
1. Run Kafka server (Make sure the Kafka server is up and running)
2. Run the application (run the main class from IntelliJ).
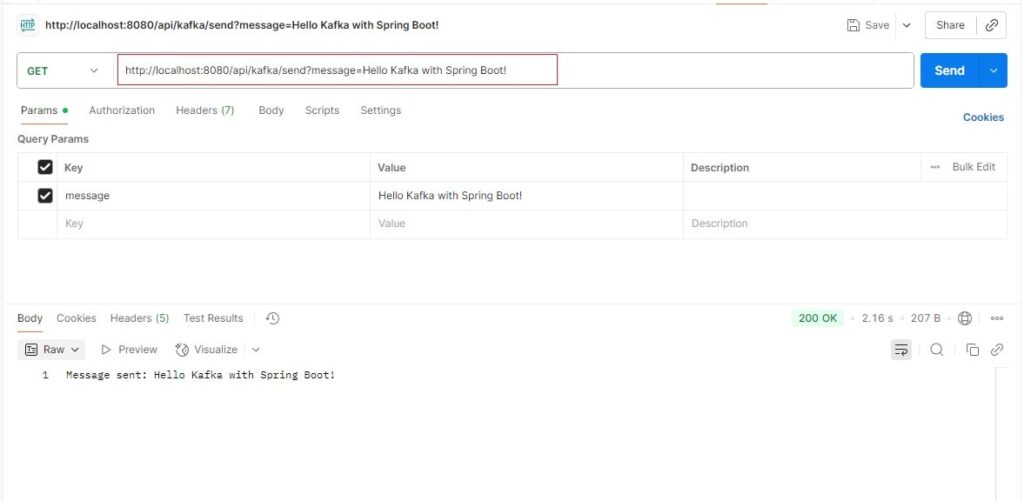
3. Open Postman → Click New → Select HTTP Request.
- Select the GET method.
- Enter URL:
http://localhost:8080/api/kafka/send?message=Hello Kafka with Spring Boot! - Click Send.
If you don’t have Postman installed, please follow this Guide: Install Postman
Now check your logs in the IntelliJ console. The consumer should print:
Received message: Hello Kafka with Spring Boot!
Common Pitfalls & Troubleshooting
- Broker not running: Ensure Zookeeper & Kafka are running before starting Spring Boot.
- Wrong bootstrap-servers: Verify
localhost:9092is correct for your Kafka instance. - Group ID conflicts: Always use unique group IDs for separate consumers.
Conclusion
In this Spring Boot Kafka integration tutorial, we covered:
- How to set up Kafka locally or with Docker
- How to create a Spring Boot Kafka project using Spring Initializr
- Importing the project into IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition
- Writing a Kafka producer and consumer with minimal configuration
- Common pitfalls and fixes
Now that you understand the basics of the Kafka producer-consumer example in Spring Boot, you can extend this by sending JSON objects, handling retries, or scaling with multiple consumer groups.
Want to revisit the lessons or explore more?
Whether you want to review a specific topic or go through the full tutorial again, everything is structured to help you master Apache Kafka step by step.
