How to Use Postman: Are you new to API testing and want to practice without setting up a backend? That’s where mock APIs come in handy! Using Postman with online mock APIs allows developers and testers to learn API workflows, practice CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete), and prototype applications without needing a real server.

In this Postman mock API tutorial, we’ll walk you through step by step:
- What is Postman, and why use mock APIs
- How to install and set up Postman
- Finding and selecting free mock APIs (JSONPlaceholder, ReqRes, Mocky)
- Creating GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE requests in Postman
- Viewing responses, headers, and status codes
Table of Contents
What is Postman and Why Use Mock APIs
Postman is a powerful API testing and development tool that lets you send requests to APIs, view responses, and automate workflows.
But what if you don’t have an API backend yet? That’s where mock APIs are useful.
Benefits of using mock APIs in Postman:
- Learn API basics without coding a backend
- Test API workflows in a safe environment
- Practice CRUD operations (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
- Prototype applications before building real APIs
How to Install and Set Up Postman
Postman is available on Windows, macOS, and Linux, as well as a web version.
- Download Postman from the official site: https://www.postman.com/downloads/
- Install and create a free account
- Open the app and you’re ready to start testing APIs
For detailed installation steps, refer to our guide: How to Install and Set Up Postman – A Complete Guide for Beginners
Finding and Selecting Free Mock APIs for Postman
Here are some popular free mock APIs you can use in Postman:
- JSONPlaceholder – A fake online REST API for testing.
- Base URL:
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/ - Example:
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts
- Base URL:
- ReqRes – A simple API with realistic responses.
- Base URL:
https://reqres.in/api/ - Example:
https://reqres.in/api/users
- Base URL:
These APIs are free and publicly available, making them perfect for practicing with Postman.
How to Use Postman – Creating API Requests in Postman
Now let’s use Postman to send different types of requests to mock APIs.
Step 1: Create a New Request
- Open Postman → Click New → Select HTTP Request.
- Enter the request URL (e.g.,
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts). - Choose the method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE).
Step 2: GET Request (Read Data)
- Select the GET method.
- Enter URL:
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1 - Click Send.
- You’ll receive a JSON response like the screenshot below:
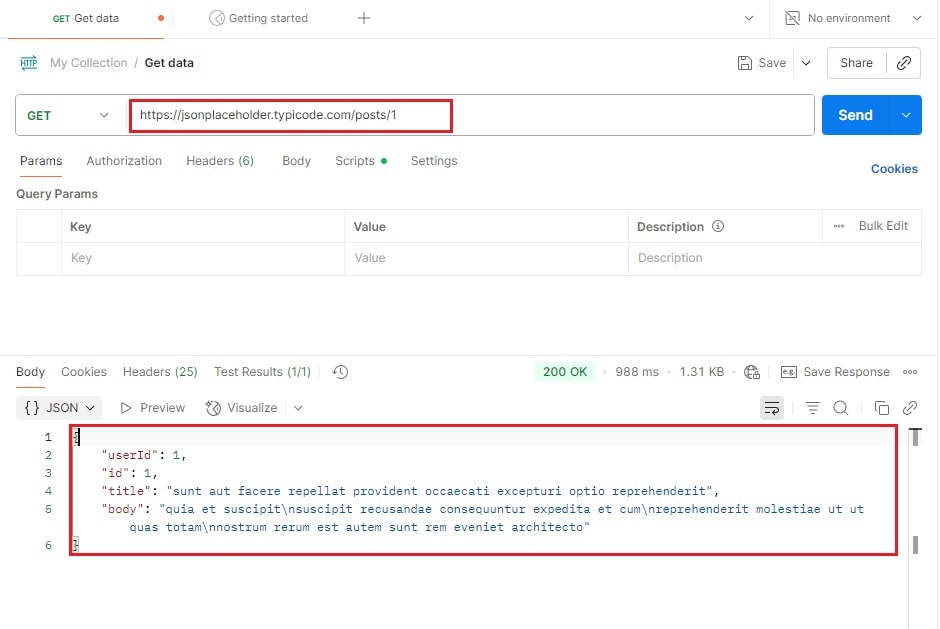
This is how you fetch data from an API using Postman.
Step 3: POST Request (Create Data)
- Select POST method.
- Enter URL:
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts - Go to Body → raw → JSON and enter:
{
"title": "New Post",
"body": "This is a test post",
"userId": 1
}
- Click Send.
- You’ll see a response with a new
idmeaning the data was created.
Step 4: PUT Request (Update Data)
- Select the PUT method.
- Enter URL:
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1 - In Body → raw → JSON, enter:
{
"id": 1,
"title": "Updated Post",
"body": "Updated content",
"userId": 1
}
- Click Send.
- The response confirms the data was updated.
Step 5: DELETE Request (Remove Data)
- Select the DELETE method.
- Enter URL:
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1 - Click Send.
- Response will be
{}or status 200, meaning the resource was deleted.
Viewing Responses, Headers, and Status Codes
When you send a request in Postman, you’ll see:
- Response Body → JSON data returned from the API
- Headers → Info like content type, server details
- Status Code →
200 OK,201 Created,404 Not Found, etc. - Response Time → How long the API took to respond
These details help you understand whether the API is working correctly.
Conclusion
In this Postman step-by-step guide for beginners, we covered:
- What Postman is and why mock APIs are useful
- Installing Postman (with a link to our installation guide)
- Free mock APIs (JSONPlaceholder, ReqRes, Mocky)
- Sending GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE requests in Postman
- Viewing API responses, headers, and status codes
With these basics, you’re now ready to explore more advanced Postman features like collections, environments, and automated testing.
